What is EVPN?
Ethernet VPN (EVPN) is a new technology that is used to extend Ethernet circuits across Data Center and Service Provider networks. It is expected to succeed other L2VPN transport methods such as BGP-based L2VPN (RFC6624), LDP-Based L2VPN (RFC4906) and VPLS.
EVPN introduces a set of new features that were not available in L2VPN and VPLS environments, most noticeable of which are All-Active Multi-homing across multiple PE devices and more efficient handling of L2 Multicast traffic.
Refer to RFC 7209 to better understand the rationale for creating EVPN.
How does EVPN work?
EVPN leverages a combination of local Data Plane learning and BGP-based Control Plane learning to share information about MAC sources within EVPN domain.
Simple EVPN topology is depicted below.
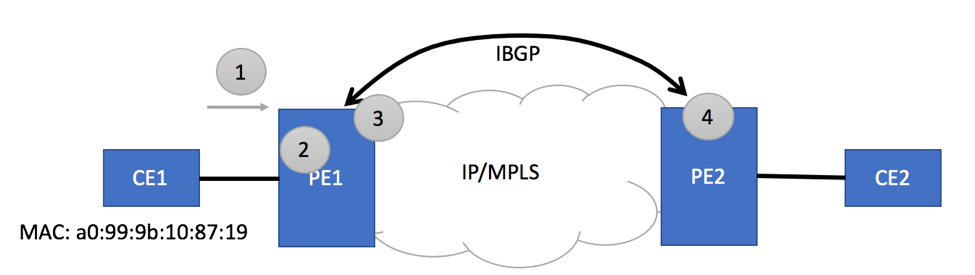
Information about MAC addresses within EVPN domain is learned and shared the following way.
- CE1 originates some traffic
- PE1 receives the traffic and populates its MAC address table with CE1’s MAC address
- PE1 advertises CE1’s MAC address via BGP to its neighbors
- Remote PE2 received BGP advertisement and populates its MAC address table with CE1’s MAC address pointing to PE1
Our example shows the most basic EVPN use case. More complex use cases might include CE multi-homing, handling of L2 Multicast traffic, L3 routing, etc.
Will EVPN replace MPLS?
MPLS is a data-plane protocol, while EVPN is a control-plane protocol. As such, EVPN will not replace MPLS. In fact, EVPN can leverage MPLS to send packets across the network.
With this being said, people often refer to Layer 3 MPLS VPN service as simple ‘MPLS’. Some new developments in EVPN (such as Type 5 routes) make it possible to replace traditional MPLS VPN service with EVPN-based service.
Do I need VXLAN to run EVPN?
You need to leverage one of the Data plane tunneling protocols in order to carry traffic across the network. VXLAN is one of the options, but it is not the only one.
As of now, EVPN can be deployed with VXLAN, MPLS (RFC 7432) or PBB (RFC7623) Data planes.
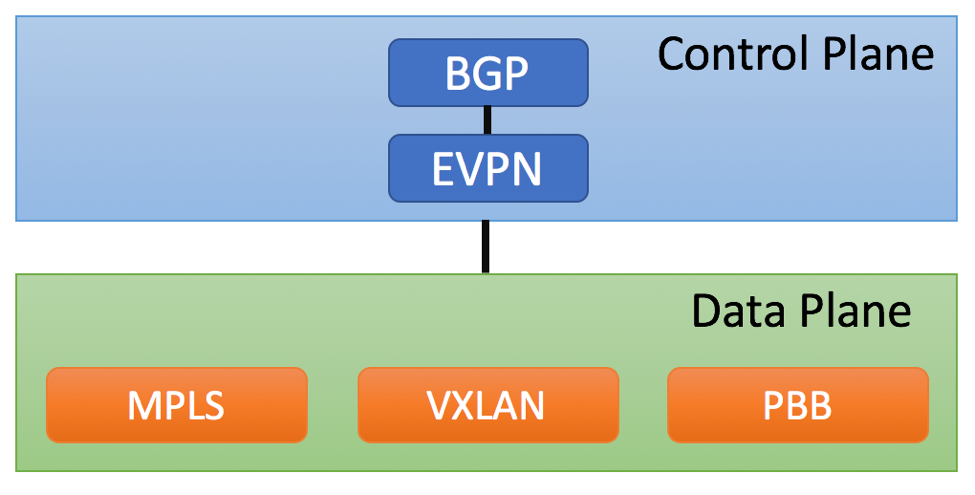
There is also work being done to introduce additional encapsulation protocols such as NVGRE and MPLS over GRE (see draft-ietf-bess-evpn-overlay-08)
Do I need BGP to run EVPN?
Yes, EVPN leverages BGP to exchange route information.
What route information is being exchanged?
EVPN RFCs and Drafts define a number of EVPN-Route types that are leveraged to exchange MAC, IP, Multicast-related information, etc. Please refer to ‘EVPN Route Types’ article for the complete list.
What are EVPN MPLS Service Types?
RFC7432 defines five different service types as shown below. These service types specify how PE devices handle broadcast domains and VLAN manipulation.
- VLAN-Based Service
- VLAN Bundle Service
- Port-Based Service
- VLAN-aware Bundle Service
- Port-based VLAN-Aware Service
Please refer to ‘EVPN MPLS Service Types’ for more information.
What are EVPN limitations?
EVPN is still undergoing active development, and as such you need to understand capabilities and limitations of the solution provided by your vendor. It is not unknown to see interoperability issues between different vendors or even within the same vendor’s portfolio.
It is also important to understand that some technical challenges have not been fully addressed by EVPN community. For example, Multicast traffic handling is a very non-trivial task and there is still no solution that would satisfy everybody’s needs.

thank you